- 226. 翻转二叉树
- 138. 复制带随机指针的链表
- 101. 对称二叉树
- 54. 螺旋矩阵
- 155. 最小栈
- 946. 验证栈序列
- 102. 二叉树的层次遍历
- 107. 二叉树的层次遍历 II
- 验证二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
226. 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:
输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
备注: 这个问题是受到 Max Howell 的 原问题 启发的 :
>谷歌:我们90%的工程师使用您编写的软件(Homebrew),但是您却无法在面试时在白板上写出翻转二叉树这道题,这太糟糕了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//pre-order traversal
void mirror(TreeNode *root){
if(!root || (!root->left && !root->right)){
return;
}
swap(root->left, root->right);
if(root->left)
mirror(root->left);
if(root->right)
mirror(root->right);
}
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
mirror(root);
return root;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了88.67% 的用户
内存消耗 :9.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了32.01%的用户
138. 复制带随机指针的链表
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的深拷贝。
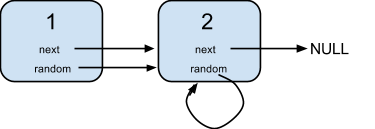
示例:
输入:
{"$id":"1","next":{"$id":"2","next":null,"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":2},"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":1}
解释:
节点 1 的值是 1,它的下一个指针和随机指针都指向节点 2 。
节点 2 的值是 2,它的下一个指针指向 null,随机指针指向它自己。
提示:
你必须返回给定头的拷贝作为对克隆列表的引用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, Node* _next, Node* _random) {
val = _val;
next = _next;
random = _random;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> mp;
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(!head){
return nullptr;
}
if(mp.find(head) == mp.end()){
mp[head] = new Node(head->val);
mp[head]->next = copyRandomList(head->next);
mp[head]->random = copyRandomList(head->random);
}
return mp[head];
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :64 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了53.88% 的用户
内存消耗 :22.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了5.58%的用户
101. 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
说明: 如果你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题,会很加分。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSame(TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right){
if(!left){
return right == nullptr;
}else if(!right){
return left == nullptr;
}
//left->left == right->right
return left->val == right->val && isSame(left->left, right->right)
&& isSame(left->right, right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root){
return true;
}
return isSame(root->left, root->right);
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :16 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了51.37% 的用户
内存消耗 :14.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了85.79%的用户
54. 螺旋矩阵
给定一个包含 m x n 个元素的矩阵(m 行, n 列),请按照顺时针螺旋顺序,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:
输入:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ]
]
输出: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:
[
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9,10,11,12]
]
输出: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> ans;
if(matrix.size() == 0){
return ans;
}
int row = matrix.size(), col = matrix[0].size();
int dir = 0, up = 0, down = row - 1, left = 0, right = col - 1,
num = row*col, x = 0, y = 0;
while(ans.size() < num){
if(dir == 0){
x = up;
for(y = left; y <= right; y++){
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
}
up++;
}else if(dir == 1){
y = right;
for(x = up; x <= down; x++){
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
}
right--;
}else if(dir == 2){
x = down;
for(y = right; y >= left; y--){
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
}
down--;
}else{
y = left;
for(x = down; x >= up; x--){
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
}
left++;
}
dir = (dir + 1)%4;
}
return move(ans);
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了59.38% 的用户
内存消耗 :8.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了52.96%的用户
155. 最小栈
设计一个支持 push,pop,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) -- 将元素 x 推入栈中。
pop() -- 删除栈顶的元素。
top() -- 获取栈顶元素。
getMin() -- 检索栈中的最小元素。
示例:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> 返回 0.
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
class MinStack {
stack<int> data;
stack<int> min;
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
data.push(x);
//take care when min stack is empty
min.push((min.empty() || x < getMin() ? x : getMin()));
}
void pop() {
if(data.empty()){
throw new exception();
}
data.pop();
min.pop();
}
int top() {
if(data.empty()){
throw new exception();
}
return data.top();
}
int getMin() {
if(data.empty()){
throw new exception();
}
return min.top();
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :44 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了81.06% 的用户
内存消耗 :17 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了31.76%的用户
946. 验证栈序列
给定 pushed 和 popped 两个序列,只有当它们可能是在最初空栈上进行的推入 push 和弹出 pop 操作序列的结果时,返回 true;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,5,3,2,1]
输出:true
解释:我们可以按以下顺序执行:
push(1), push(2), push(3), push(4), pop() -> 4,
push(5), pop() -> 5, pop() -> 3, pop() -> 2, pop() -> 1
示例 2:
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,3,5,1,2]
输出:false
解释:1 不能在 2 之前弹出。
提示: 0 <= pushed.length == popped.length <= 1000 0 <= pushed[i], popped[i] < 1000 pushed 是 popped 的排列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
stack<int> st;
auto it_pushed = pushed.begin(), it_poped = popped.begin();
while(it_pushed != pushed.end() || it_poped != popped.end()){
//if push sequence is valid
if(it_pushed != pushed.end() && (st.empty() || st.top() != *it_poped)){
st.push(*it_pushed);
it_pushed++;
//if pop sequence is valid
}else if(it_poped != popped.end() && st.top() == *it_poped){
st.pop();
it_poped++;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :12 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了88.03% 的用户
内存消耗 :9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了80.69%的用户
102. 二叉树的层次遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回其按层次遍历的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
例如:
给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if(!root) return ans;
queue<TreeNode *> Q;
Q.push(root);
int level = 0;
while(!Q.empty()){
if(ans.size() <= level){
ans.push_back(vector<int>{});
}
int num = Q.size();
while(num--){
auto node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
ans[level].push_back(node->val);
if(node->left) Q.push(node->left);
if(node->right) Q.push(node->right);
}
level++;
}
return move(ans);
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了90.97% 的用户
内存消耗 :13.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了99.00%的用户
107. 二叉树的层次遍历 II
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其自底向上的层次遍历为:
[
[15,7],
[9,20],
[3]
]
解题思路:将层序遍历结果反序输出。
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了94.54% 的用户
内存消耗 :13.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了98.66%的用户
验证二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
bool verifySequenceOfBST(vector<int> &seq, int beg, int end){
if(seq.size() == 0){
return false;
}else if(seq.size() == 1){
return true;
}
int root = *seq.rbegin();
int left = beg;
for(; left < end; left++){
if(seq.at(left) > root)
break;
}
int right = left;
for(; right < end; right++){
if(seq.at(right) < root)
return false;
}
if(left > 0 && !verifySequenceOfBST(seq, beg, left)){
return false;
}
if(right < end - 1 && !verifySequenceOfBST(seq, left + 1, right)){
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool verifySequenceOfBST(vector<int> &seq){
return verifySequenceOfBST(seq, 0, seq.size() - 1);
}
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
if(inorder.size() != postorder.size() || inorder.size() == 0){
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(*postorder.rbegin());
if(inorder.size() == 1){
return root;
}
auto mid = find(inorder.begin(), inorder.end(), *postorder.rbegin());
vector<int> inleft(inorder.begin(), mid), //[first, last)
inright(mid + 1, inorder.end()),
postleft, postright;
//build left/right post order seq
for(auto it = postorder.begin(); it < postorder.end() - 1; it++){
if(find(inleft.begin(), inleft.end(), *it) != inleft.end()){
postleft.push_back(*it);
}else{
postright.push_back(*it);
}
}
root->left = buildTree(inleft, postleft);
root->right = buildTree(inright, postright);
return root;
}
};
测试一下,由于每一颗子树都要复制序列数组,在测试大数据量用例时会超时。
执行结果:
超出时间限制
显示详情
最后执行的输入:
[-999,-998,-997,-996,-995,-994,-993,-992,-991,-990,-989,-988,-987,-986,-985,-984,-983,-982,-981,-980,-979,-978,-977,-976,-975,-974,-973,-972,-971,....
查看全部
C++里没有数组的概念,用Go来写这道题,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
var root *TreeNode
if len(inorder) != len(postorder) || len(postorder) == 0 {
return root
}
rootVal := postorder[len(postorder)-1]
root = &TreeNode{Val:rootVal}
if len(postorder) == 0 {
return root
}
var idx int
for ; idx < len(postorder)-1; idx++ {
if inorder[idx] == rootVal {
break
}
}
root.Left = buildTree(inorder[:idx], postorder[:idx])
root.Right = buildTree(inorder[idx+1:], postorder[idx:len(postorder)-1])
return root
}
测试一下,这次我们没有做多余的序列复制,因此通过了测试。
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :36 ms, 在所有 Go 提交中击败了81.93% 的用户
内存消耗 :24.8 MB, 在所有 Go 提交中击败了18.18%的用户