- 50. Pow(x, n)
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 876. 链表的中间结点
- 141. 环形链表
- 142. 环形链表 II
- 206. 反转链表
- 92. 反转链表 II
- 21. 合并两个有序链表
- 23. 合并K个排序链表
- 572. 另一个树的子树
50. Pow(x, n)
实现 pow(x, n) ,即计算 x 的 n 次幂函数。
示例 1:
输入: 2.00000, 10
输出: 1024.00000
示例 2:
输入: 2.10000, 3
输出: 9.26100
示例 3:
输入: 2.00000, -2
输出: 0.25000
解释: 2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
说明: -100.0 < x < 100.0 n 是 32 位有符号整数,其数值范围是 [−231, 231 − 1] 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
//corner case
if(x == 1){
return x;
}else if(x == -1){
return n & 0x01 ? x : -x;
}else if(n == 0){
return 1;
}else if(n == 1){
return x;
}else if(n == INT_MIN){
return 0.0; //-INT_MIN will be out of range
}
bool sign = n > 0 ? false : true;
n = abs(n);
//2^6 -> calc 2^3 first
double res = myPow(x, n >> 1);
//2^3 * 2^3
res *= res;
if(n & 0x1 == 1){
// 2^7 = 2^3 * 2^3 * 2
res *= x;
}
if(sign && res != 0){
return 1/res;
}else{
return res;
}
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
执行用时 :4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了90.99% 的用户
内存消耗 :8.3 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了81.51%的用户
19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
说明:
给定的 n 保证是有效的。
进阶:
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
if(!head){
return head;
}
auto dummy = ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
auto prv = &dummy, cur = head, nxt = head;
//advance n node first
while(n-- && nxt){
nxt = nxt->next;
}
while(nxt){
prv = cur;
cur = cur->next;
nxt = nxt->next;
}
prv->next = cur->next;
delete cur;
return dummy.next;
}
};
876. 链表的中间结点
给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
示例 1:
输入:[1,2,3,4,5]
输出:此列表中的结点 3 (序列化形式:[3,4,5])
返回的结点值为 3 。 (测评系统对该结点序列化表述是 [3,4,5])。
注意,我们返回了一个 ListNode 类型的对象 ans,这样:
ans.val = 3, ans.next.val = 4, ans.next.next.val = 5, 以及 ans.next.next.next = NULL.
示例 2:
输入:[1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:此列表中的结点 4 (序列化形式:[4,5,6])
由于该列表有两个中间结点,值分别为 3 和 4,我们返回第二个结点。
提示: 给定链表的结点数介于 1 和 100 之间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
// 0 0 0 0
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
auto fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了86.11% 的用户
内存消耗 :8.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了9.20%的用户
141. 环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
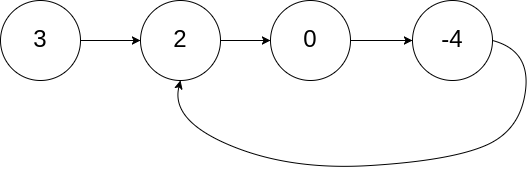
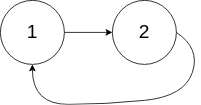

进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
auto fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :20 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了61.32% 的用户
内存消耗 :9.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了76.31%的用户
142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
例子同上题,
使用额外空间,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_set<ListNode *> nxt;
while(head){
if(nxt.count(head) > 0){
return head;
}else{
nxt.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :24 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了38.00% 的用户
内存消耗 :11.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了10.90%的用户
不使用额外空间,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(!head) {
return nullptr;
}
//check if cycle exists
auto slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast){
break;
}
}
if(!fast || !fast->next){
return nullptr;
}
//check the joint node
slow = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :24 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了38.00% 的用户
内存消耗 :9.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了99.06%的用户
206. 反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶: 你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next){
return head;
}
ListNode *curr = head, *next = nullptr, *prev = nullptr;
while(curr->next){
next = curr->next; //prev <- curr -> next ->
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next; // prev curr
}
curr->next = prev;
return curr;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了99.28% 的用户
内存消耗 :9.2 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了16.66%的用户
92. 反转链表 II
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
//function to reverse list
auto reverseList = [](ListNode *head) -> ListNode *{
if(!head){
return head;
}
ListNode *cur = head, *prev = nullptr, *next = nullptr;
while(cur){
next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
};
//no need to do reverse
if(m == n || !head || !head->next){
return head;
}
ListNode dummy(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode *pre_first = nullptr, *first = nullptr,
*aft_last = nullptr, *cur = head, *prev = &dummy;
int cnt = 1;
//find the seprate point
while(cur && cnt < n){
if(cnt == m){
pre_first = prev;
first = cur;
cout<<first->val<<endl;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
cnt++;
}
cout<<endl;
if(cur) aft_last = cur->next;
//seprate the list in [m:n]
pre_first->next = nullptr;
if(cur) cur->next = nullptr;
//reverse the list in [m:n]
first = reverseList(first);
//link the list in [:m]
pre_first->next = first;
//link the list in [n:] if exists
if(aft_last){
while(first->next){
first = first->next;
cout<<first->val<<" ";
}
first->next = aft_last;
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了72.42% 的用户
内存消耗 :8.5 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了92.20%的用户
21. 合并两个有序链表
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummy(INT_MAX);
auto prev = &dummy;
while(l1 || l2){
if(l1 && l2){
if(l1->val <= l2->val){
prev->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}else{
prev->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}else if(l1){
prev->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}else{
prev->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
prev = prev->next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :8 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了98.86% 的用户
内存消耗 :8.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了86.77%的用户
23. 合并K个排序链表
合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。请分析和描述算法的复杂度。
示例:
输入:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
输出: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
if(lists.size() == 0){
return nullptr;
}else if(lists.size() == 1){
return *lists.begin();
}
ListNode *head = mergeTwoLists(lists[0], lists[1]);
for(int i = 2; i < lists.size(); i++){
head = mergeTwoLists(head, lists[i]);
}
return head;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :356 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了16.49% 的用户
内存消耗 :10.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
572. 另一个树的子树
给定两个非空二叉树 s 和 t,检验 s 中是否包含和 t 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。s 的一个子树包括 s 的一个节点和这个节点的所有子孙。s 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
示例 1:
给定的树 s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
给定的树 t:
4
/ \
1 2
返回 true,因为 t 与 s 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
示例 2:
给定的树 s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
/
0
给定的树 t:
4
/ \
1 2
返回 false。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode *s, TreeNode *t){
if(!s && !t){
return true;
}else if(!s || !t){
return false;
}
return s->val == t->val && isSameTree(s->left, t->left) &&
isSameTree(s->right, t->right);
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) {
bool result = false;
if(!s || !t){
return result;
}
if(s->val == t->val){
result = isSameTree(s, t);
}
if(!result){
result = isSubtree(s->left, t) || isSubtree(s->right, t);
}
return result;
}
};
测试一下,
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时 :36 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了88.75% 的用户
内存消耗 :20.8 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了93.36%的用户